Learn how to build an Arduino-based obstacle avoiding robot step by step using an ultrasonic sensor, servo motor, and the Adafruit Motor Shield. This project teaches you the basics of autonomous navigation and motor control, helping your robot detect and avoid obstacles automatically. Perfect for beginners in robotics, this guide includes the full Arduino code, wiring connections, and calibration tips to get your robot running smoothly.
Step 1: Required Components and Hardwares

- Arduino UNO R3 – https://amzn.to/42Lfm1F
- L293D Motor Shield – https://amzn.to/4qoI0Qo
- HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Module Distance Sensor for Arduino – https://amzn.to/42Royl3
- SG90 9G Micro Servo Motor – https://amzn.to/43umW0O
- Bracket for HC-SR04 – https://amzn.to/42N61GB
- Dual DC 3-6V Gearbox Motor Motor and Wheels – https://amzn.to/4niyzPI
- Bovine Bearing Wheel – https://amzn.to/4namkEz
- DIY Arduino Robot Car Chassis Kit – https://amzn.to/4qhBfzx
- Jumper Ribbon Cables Kit – https://amzn.to/4qkOSOq
- Battery Connector 9V – https://amzn.to/4nVEoU9
- Zip Ties – https://amzn.to/4qoHbHm
Step 2: Circuit Diagram – Wiring and Hardware Setup
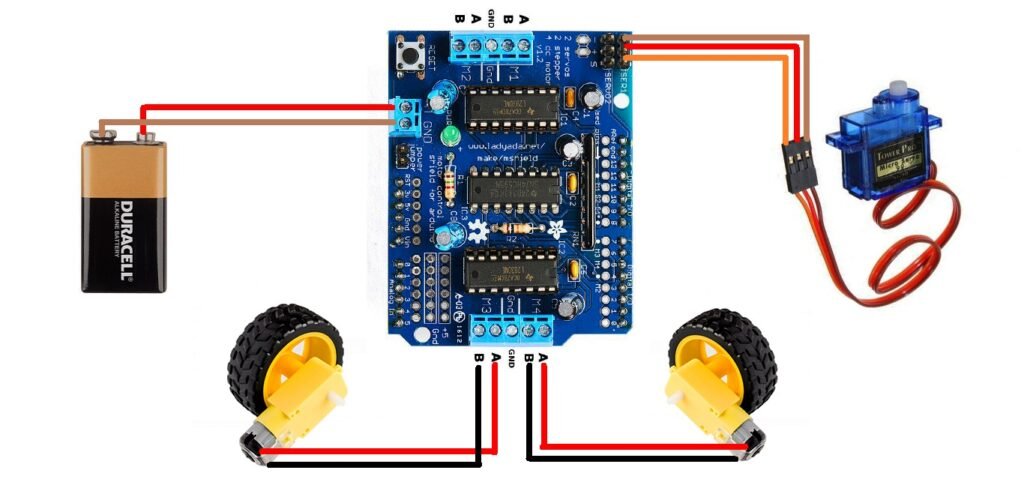
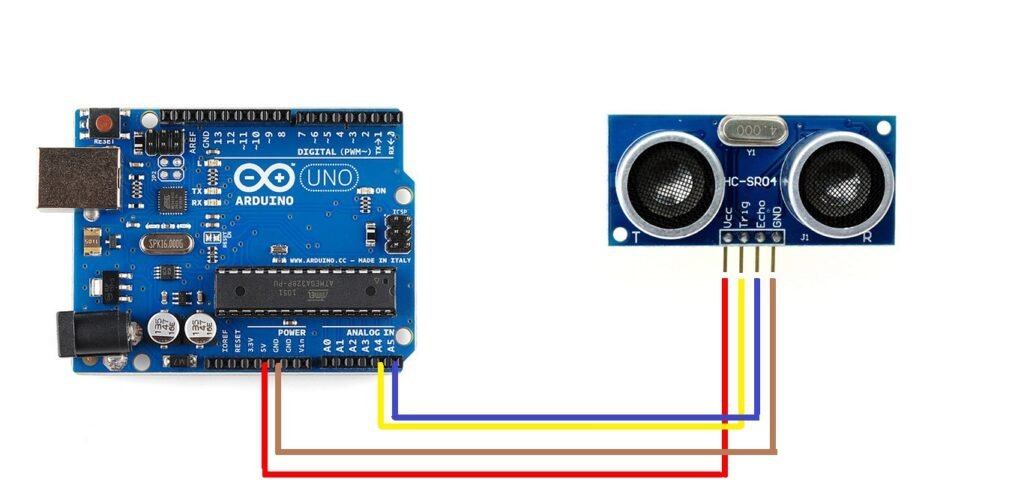
Connect your components according to the following guide:
- Ultrasonic Trigger → A0 (sends signal)
- Ultrasonic Echo → A1 (receives signal)
- Servo (signal wire) → D10 (rotates ultrasonic sensor)
- Left Motor → M1 on Motor Shield (left wheels)
- Right Motor → M2 on Motor Shield (right wheels)
- Motor Shield → Mounted on top of Arduino
- Power → External 6–9V battery (Do NOT power motors via USB)
Tip: The ultrasonic sensor, motors, and Arduino must share a common GND connection.
Step 3: Source Code
Required Libraries
Before uploading the code, make sure you install the following Arduino libraries:
- AFMotor: Controls DC motors using the Adafruit Motor Shield. Go to Sketch → Include Library → Manage Libraries… and search for “Adafruit Motor Shield Library”.
- Servo: Included by default with the Arduino IDE. No need to install separately.
- NewPing: For accurate ultrasonic distance measurements. Search for “NewPing” in the Library Manager and install it.
Uploading the Code
- Open the Arduino IDE.
- Copy and paste the obstacle avoiding robot code.
- Select the correct Board (for example, Arduino Uno) and Port.
- Click Upload.
- After uploading, the servo should move slightly when the robot powers up.
First Power-On Test
Before placing the robot on the floor, check the following:
- Servo Test: The ultrasonic sensor should rotate right (around 144 degrees), then left (around 36 degrees), and finally center (90 degrees). If it moves in the opposite direction, remove the servo horn and reattach it rotated 180 degrees.
- Motor Test: The robot should move forward when both motors spin in the same direction. If it moves backward, swap the motor wires on the motor shield.
Calibration and Fine-Tuning
You may need to adjust the following constants inside the code for smoother motion:
- COLL_DIST – Minimum distance before stopping (recommended 15–25 cm)
- TURN_DIST – Distance to start turning slightly (recommended 25–35 cm)
- MOTORS_CALIBRATION_OFFSET – Balances left and right motor speed (−5 to +5)
- MAX_SPEED – Maximum motor speed (PWM 0–255, recommended 120–180)
Adjust one variable at a time, test again, and observe how the robot reacts.
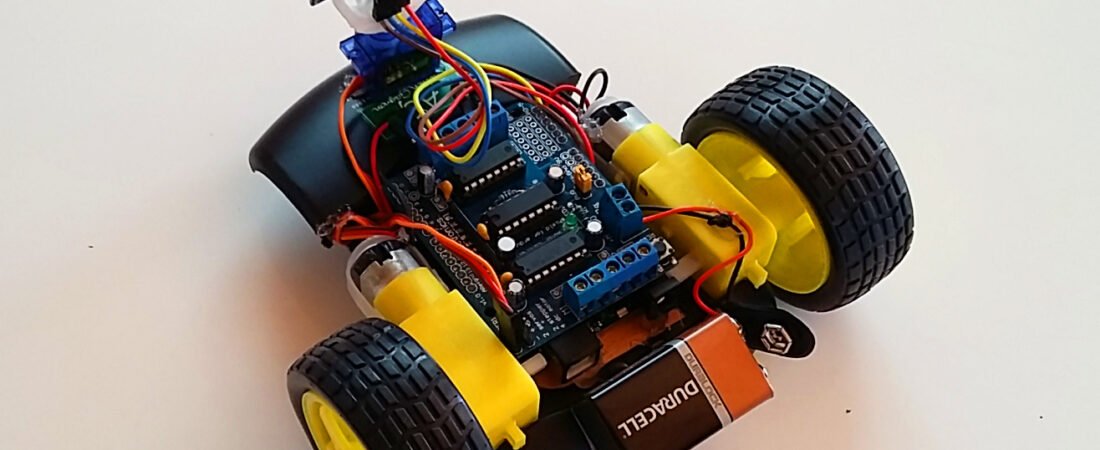
Testing in Action
- Place your robot on a flat, open surface.
- Power it on – the servo should scan left and right, and the robot should start moving forward.
- Place an object (like a small box) in front of it – the robot should stop, move backward, and turn away.
- Try it in narrow corridors or near walls to see how it adapts.
- If the robot reacts too early or too late, adjust the COLL_DIST and TURN_DIST values.
/*
Arduino: How to Build an Obstacle Avoiding Robot (Fixed & Commented)
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Hardware:
- Arduino + Adafruit Motor Shield v1 (AFMotor)
- 2x DC motors (M1 = left, M2 = right)
- Ultrasonic sensor (HC-SR04) with NewPing
- Servo on D10 to rotate the ultrasonic "neck"
Behavior:
- Servo sweeps: Right (144°) -> Left (36°)
- Reads distance at each step
- If too close: back up and turn toward the most open angle
- If getting close: make small steering nudges away from the obstacle
- Else: keep moving forward with smooth acceleration
*/
#include <AFMotor.h>
#include <Servo.h>
#include <NewPing.h>
// --- Ultrasonic pins and limits ---
#define TRIG_PIN A0
#define ECHO_PIN A1
#define MAX_DISTANCE_POSSIBLE 100 // cm, NewPing cap
// --- Motion & tuning constants ---
#define MAX_SPEED 160 // 0-255; keep headroom for control
#define MOTORS_CALIBRATION_OFFSET 3 // Straight-line trim between motors
#define COLL_DIST 20 // <= this: treat as collision (cm)
#define TURN_DIST (COLL_DIST + 10) // caution zone; start path nudges
NewPing sonar(TRIG_PIN, ECHO_PIN, MAX_DISTANCE_POSSIBLE);
// --- Motors & servo ---
AF_DCMotor leftMotor(1, MOTOR12_8KHZ);
AF_DCMotor rightMotor(2, MOTOR12_8KHZ);
Servo neckControllerServoMotor; // D10
// --- State variables ---
int pos = 0;
int maxDist = 0; // farthest distance found in current sweep
int maxAngle = 90; // angle where farthest distance was found
int maxRight = 0; // right sector best
int maxLeft = 0; // left sector best
int maxFront = 0; // front best
int course = 0; // (unused)
int curDist = 0; // last read distance
String motorSet = "";
int speedSet = 0;
void setup() {
neckControllerServoMotor.attach(10);
neckControllerServoMotor.write(90); // center forward
delay(2000);
checkPath(); // initial scan
motorSet = "FORWARD";
neckControllerServoMotor.write(90);
moveForward();
}
void loop() {
checkForward(); // keep motors aligned with "FORWARD" state
checkPath(); // scan and respond continuously
}
// Sweep servo 144 -> 36 by 18-degree steps; collect distances.
// Decide on immediate reactions (backup/turn or small nudges).
void checkPath() {
int curLeft = 0;
int curFront = 0;
int curRight = 0;
// Reset best-of-sweep trackers
maxDist = -1;
maxAngle = 90;
neckControllerServoMotor.write(144); // start from right
delay(120);
for (pos = 144; pos >= 36; pos -= 18) {
neckControllerServoMotor.write(pos);
delay(90); // let servo settle
checkForward(); // keep rolling if safe
curDist = readPing(); // cm
// Immediate obstacle very close: back up, stop, decide turn, then break
if (curDist <= COLL_DIST) {
checkCourse();
break;
}
// Getting close: preemptively nudge AWAY from the obstacle side
if (curDist <= TURN_DIST) {
changePath(); // now steers away from current side (fixed)
}
// Track the farthest free angle during this sweep (fixed)
if (curDist > maxDist) {
maxDist = curDist;
maxAngle = pos;
}
// Aggregate sector maxima based on angle map:
// 144° ~ right, 90° ~ front, 36° ~ left
if (pos > 90 && curDist > curRight) { curRight = curDist; }
if (pos == 90 && curDist > curFront) { curFront = curDist; }
if (pos < 90 && curDist > curLeft) { curLeft = curDist; }
}
// Expose for other routines (optional analytics/telemetry)
maxLeft = curLeft;
maxRight = curRight;
maxFront = curFront;
}
// Decide a new heading toward the most open side.
// Angle map: <90 = left sector, >90 = right sector.
void setCourse() {
if (maxAngle < 90) { turnLeft(); } // FIXED: left angle -> turn left
else if (maxAngle > 90) { turnRight(); } // FIXED: right angle -> turn right
// If exactly 90 (front), keep forward state; no explicit action.
// Reset cached maxima
maxLeft = 0;
maxRight = 0;
maxFront = 0;
}
// Emergency: back up, stop, then pick the best direction.
void checkCourse() {
moveBackward();
delay(500);
moveStop();
setCourse();
}
// Small corrective nudge AWAY from where we are currently looking (FIXED)
// If servo is left (<90), obstacle likely left-ish -> nudge RIGHT
// If servo is right (>90), obstacle likely right-ish -> nudge LEFT
void changePath() {
if (pos < 90) { lookRight(); }
if (pos > 90) { lookLeft(); }
}
// Robust ultrasonic read: treat 0 (no echo) as "very far"
int readPing() {
delay(70);
unsigned int uS = sonar.ping();
int cm = uS / US_ROUNDTRIP_CM;
if (cm == 0) cm = MAX_DISTANCE_POSSIBLE; // no echo -> assume far
return cm;
}
// Keep motors consistent with the desired state
void checkForward() { if (motorSet == "FORWARD") { leftMotor.run(FORWARD); rightMotor.run(FORWARD); } }
void checkBackward() { if (motorSet == "BACKWARD") { leftMotor.run(BACKWARD); rightMotor.run(BACKWARD); } }
// Immediate stop
void moveStop() { leftMotor.run(RELEASE); rightMotor.run(RELEASE); }
// Smooth forward ramp
void moveForward() {
motorSet = "FORWARD";
leftMotor.run(FORWARD);
rightMotor.run(FORWARD);
for (speedSet = 0; speedSet < MAX_SPEED; speedSet += 2) {
leftMotor.setSpeed(speedSet + MOTORS_CALIBRATION_OFFSET);
rightMotor.setSpeed(speedSet);
delay(5);
}
}
// Smooth backward ramp
void moveBackward() {
motorSet = "BACKWARD";
leftMotor.run(BACKWARD);
rightMotor.run(BACKWARD);
for (speedSet = 0; speedSet < MAX_SPEED; speedSet += 2) {
leftMotor.setSpeed(speedSet + MOTORS_CALIBRATION_OFFSET);
rightMotor.setSpeed(speedSet);
delay(5);
}
}
// In-place right turn (spin)
void turnRight() {
motorSet = "RIGHT";
leftMotor.run(FORWARD);
rightMotor.run(BACKWARD);
delay(400);
motorSet = "FORWARD";
leftMotor.run(FORWARD);
rightMotor.run(FORWARD);
}
// In-place left turn (spin)
void turnLeft() {
motorSet = "LEFT";
leftMotor.run(BACKWARD);
rightMotor.run(FORWARD);
delay(400);
motorSet = "FORWARD";
leftMotor.run(FORWARD);
rightMotor.run(FORWARD);
}
// Tiny corrective taps to bias heading while moving
void lookRight() { rightMotor.run(BACKWARD); delay(400); rightMotor.run(FORWARD); }
void lookLeft() { leftMotor.run(BACKWARD); delay(400); leftMotor.run(FORWARD); }
Troubleshooting Tips
- Robot does not move – Check your battery level; motors require at least 6V.
- Robot always turns one way – Adjust MOTORS_CALIBRATION_OFFSET.
- No distance readings – Ensure ultrasonic sensor pins (A0 and A1) are correctly connected.
- Robot stops randomly – Replace or recharge the battery; low voltage causes instability.

Bir yanıt yazın