In this tutorial, you will learn how to control a servo motor using an Arduino and a smartphone via Bluetooth. The Bluetooth connection allows you to send position commands (0–180 degrees) wirelessly using a custom Android app built with MIT App Inventor.
The app includes both buttons and a slider, allowing you to rotate the servo motor to different positions easily.
Important Advices:
- Before uploading the code, remove the VCC cable from the Bluetooth module.
- If you use the HC-05 Bluetooth module, it will ask for a PIN code — usually 1234 or 0000.
- If you get an error such as ERROR 507 or 516 broken pipe, try reconnecting a few times — the connection may occasionally drop.
- Make sure that your Arduino or Genuino board is connected to your computer via USB when uploading the sketch or monitoring serial data.
- Always include the SoftwareSerial library for Bluetooth communication.
- I recommend you do not connect the servo motor directly to the Arduino’s 5V pin. Use an external 5V power supply for safety and stable operation.
The SG90 Mini RC servo can be powered from Arduino for testing, but stronger servos like MG996R draw high current and may damage your board.
MG996R Specs:
- Stall Torque: 9.4 kg·cm (4.8V) – 11 kg·cm (6.0V)
- Operating Voltage: 4.8V – 6.6V
Circuit
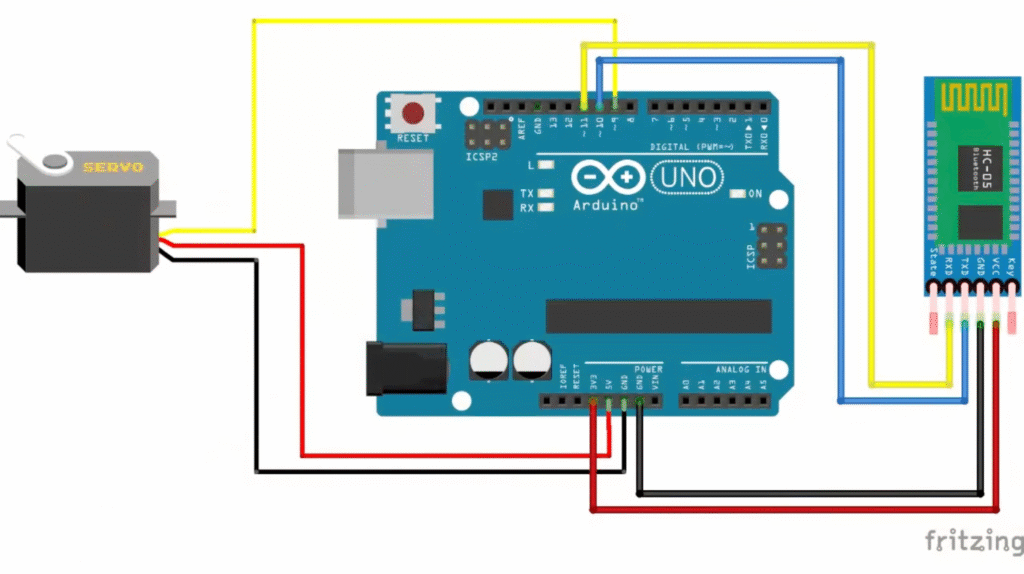
Hardware Required:
- Arduino Uno or Genuino board
- Bluetooth Module (HC-05 or HC-06)
- Servo Motor (SG90 or MG996)
- Hook-up Wires
Circuit Connections:
- Servo Motor
- Red → +5V (or external 5V supply)
- Brown/Black → GND
- Yellow/Orange → Digital Pin 9
- Bluetooth Module (HC-05)
- VCC → 5V
- GND → GND
- TX → Digital Pin 10 (Arduino RX)
- RX → Digital Pin 11 (Arduino TX)
Code
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> // Library for Bluetooth
#include <Servo.h> // Library for Servo
Servo myservo; // Create a servo object
int bluetoothTx = 10; // Bluetooth TX pin
int bluetoothRx = 11; // Bluetooth RX pin
SoftwareSerial bluetooth(bluetoothTx, bluetoothRx); // Create Bluetooth serial
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // Attach servo signal to pin 9
Serial.begin(9600); // Start Serial Monitor
bluetooth.begin(9600); // Start Bluetooth communication
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from Bluetooth
if (bluetooth.available() > 0) {
int servopos = bluetooth.read(); // Read received number
Serial.println(servopos); // Print received angle
myservo.write(servopos); // Move servo to received angle
}
}How It Works:
- The Arduino communicates with the Bluetooth module using software-based serial communication on pins 10 and 11.
- The smartphone sends numeric values (0–180) over Bluetooth.
- Arduino reads these values and sets the servo position accordingly.
- You can control the servo motor from an Android phone using slider or button inputs.
Creating the Android App (MIT App Inventor)
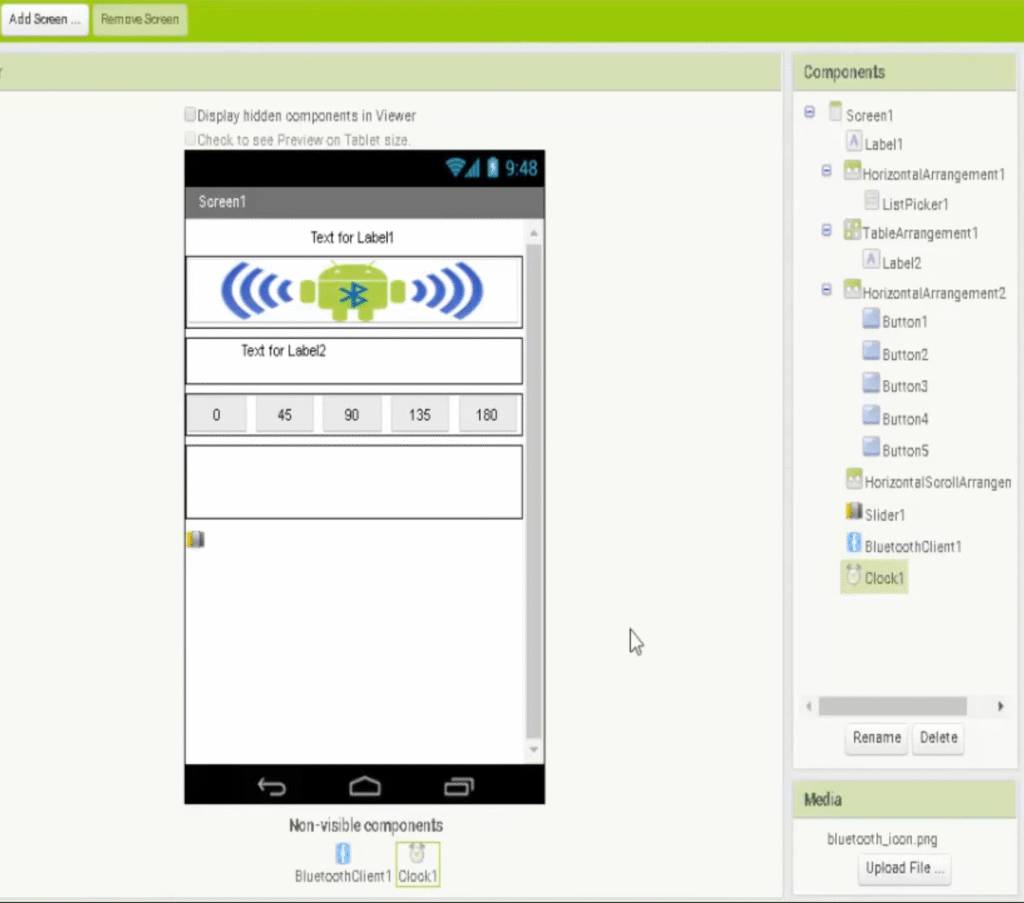
- Go to MIT App Inventor.
- Create a new project and add the following components:
- BluetoothClient
- ListPicker
- Buttons for fixed angles (0, 45, 90, 135, 180)
- Slider for continuous servo control
- Labels for connection and position status
- Clock component to monitor Bluetooth connection
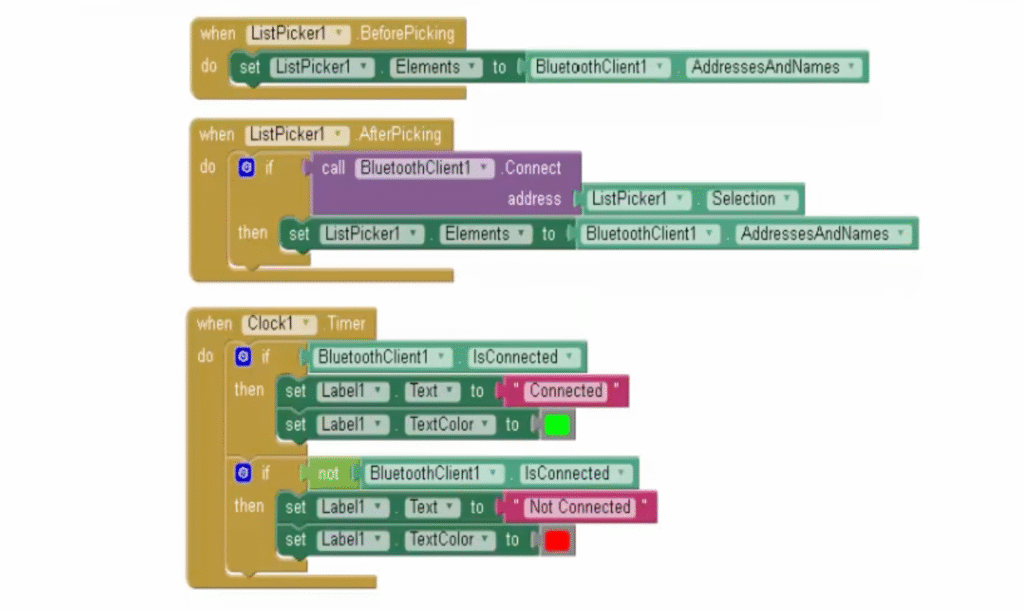

- Use the Blocks Editor to set up your app logic:
- Use the ListPicker to select and connect to the HC-05 module.
- Buttons send preset servo angles (0, 45, 90, 135, 180).
- The slider sends values dynamically between 0–180.
- Clock checks if the device remains connected.
- When finished, go to Build → App (.apk) and download it to your computer.
- Transfer the file to your Android phone or tablet.
- Enable Install from Unknown Sources in your Android settings, then install the app.
How the Android App Works:
- ListPicker1 displays all available Bluetooth devices.
- Once connected, the app changes the label to show “Connected.”
- Buttons (0, 45, 90, 135, 180) send a fixed servo angle command.
- Slider1 allows smooth control between 0° and 180°.
- The app continuously updates the connection status.
This project provides a simple and interactive way to control a servo motor wirelessly via your smartphone. You can use this concept in robotic arms, remote-controlled cars, or camera pan-tilt systems. It’s a great introduction to Bluetooth communication with Arduino and mobile app development using MIT App Inventor.

Bir yanıt yazın